Smart Info About When To Use Stacked Column Charts Chart Js Line Jsfiddle
Stacked column charts work well when the focus of the chart is to compare the totals and one part of the totals.
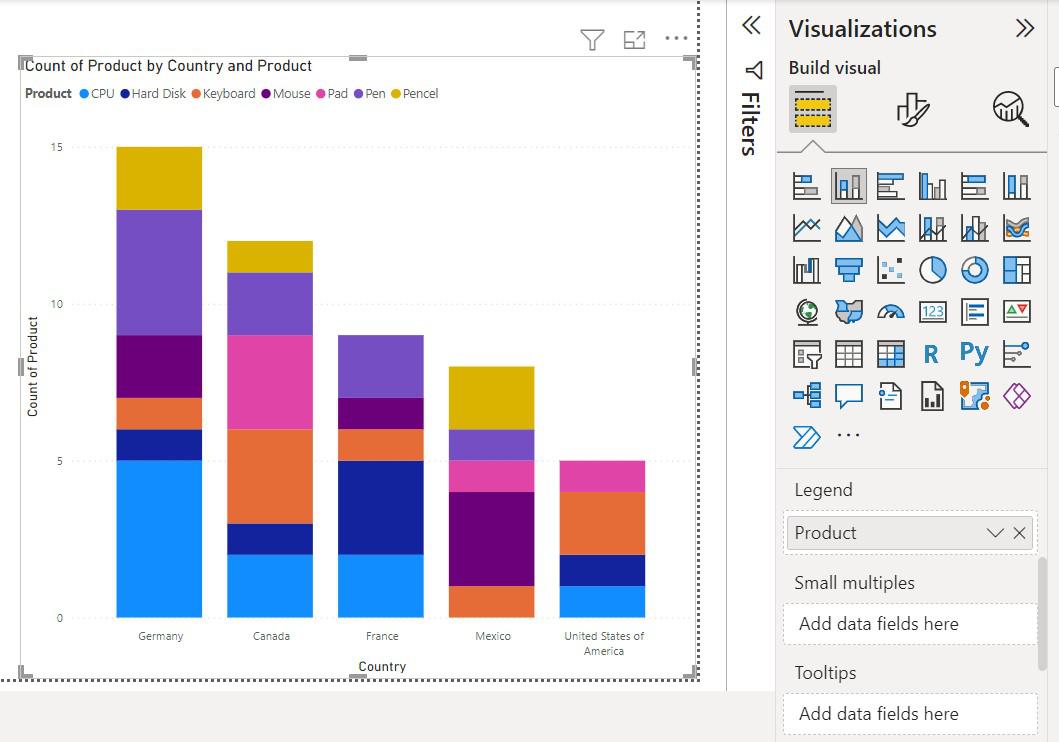
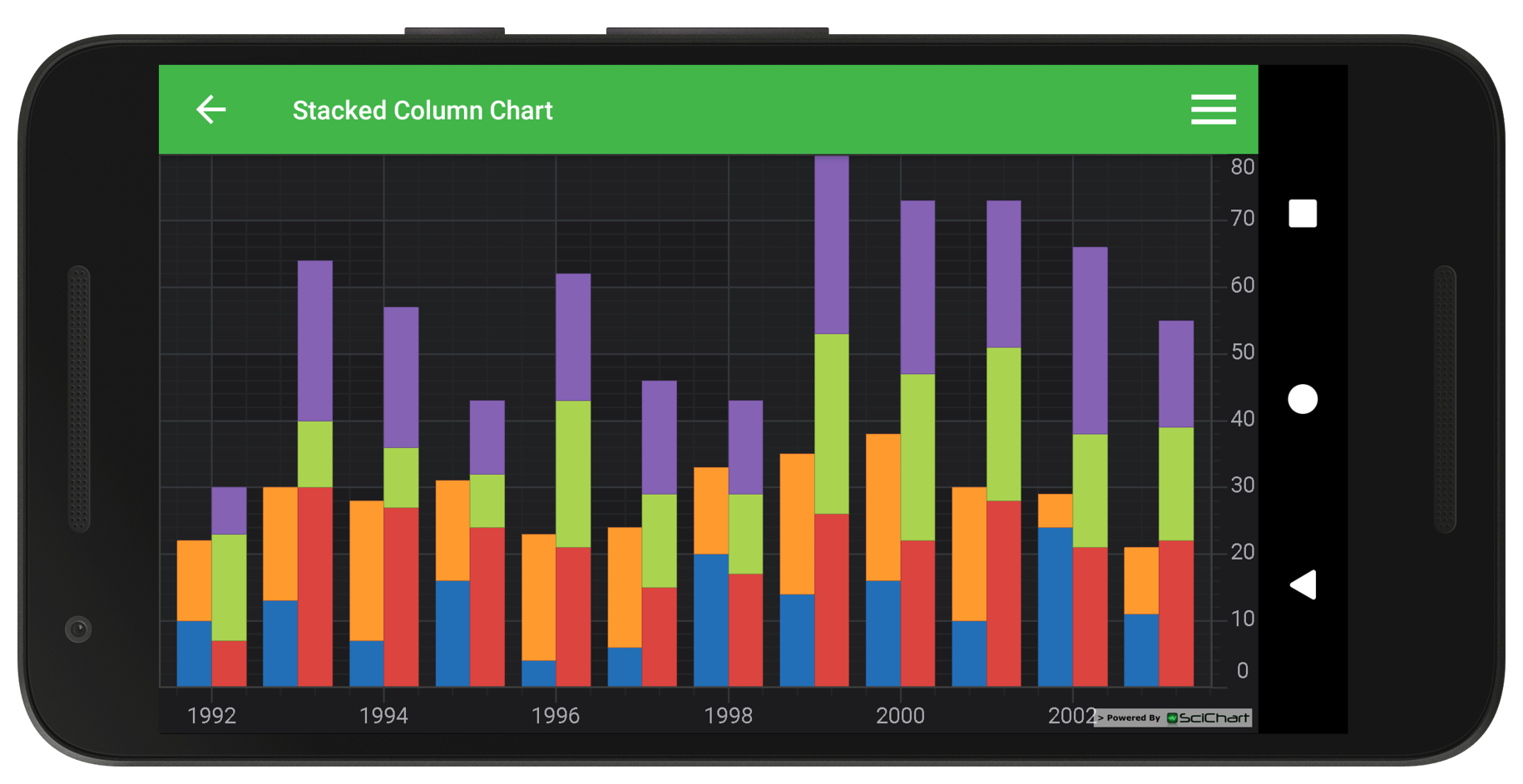
When to use stacked column charts. I am trying to create a pivot chart which represents two mutually exclusive averages. Average number of days it takes a report to get to department a (qrb). Stacked column charts are a variant of standard column charts, where the totals indicated by the height of the columns are shown using stacked segments as a sum of various contributing categories.
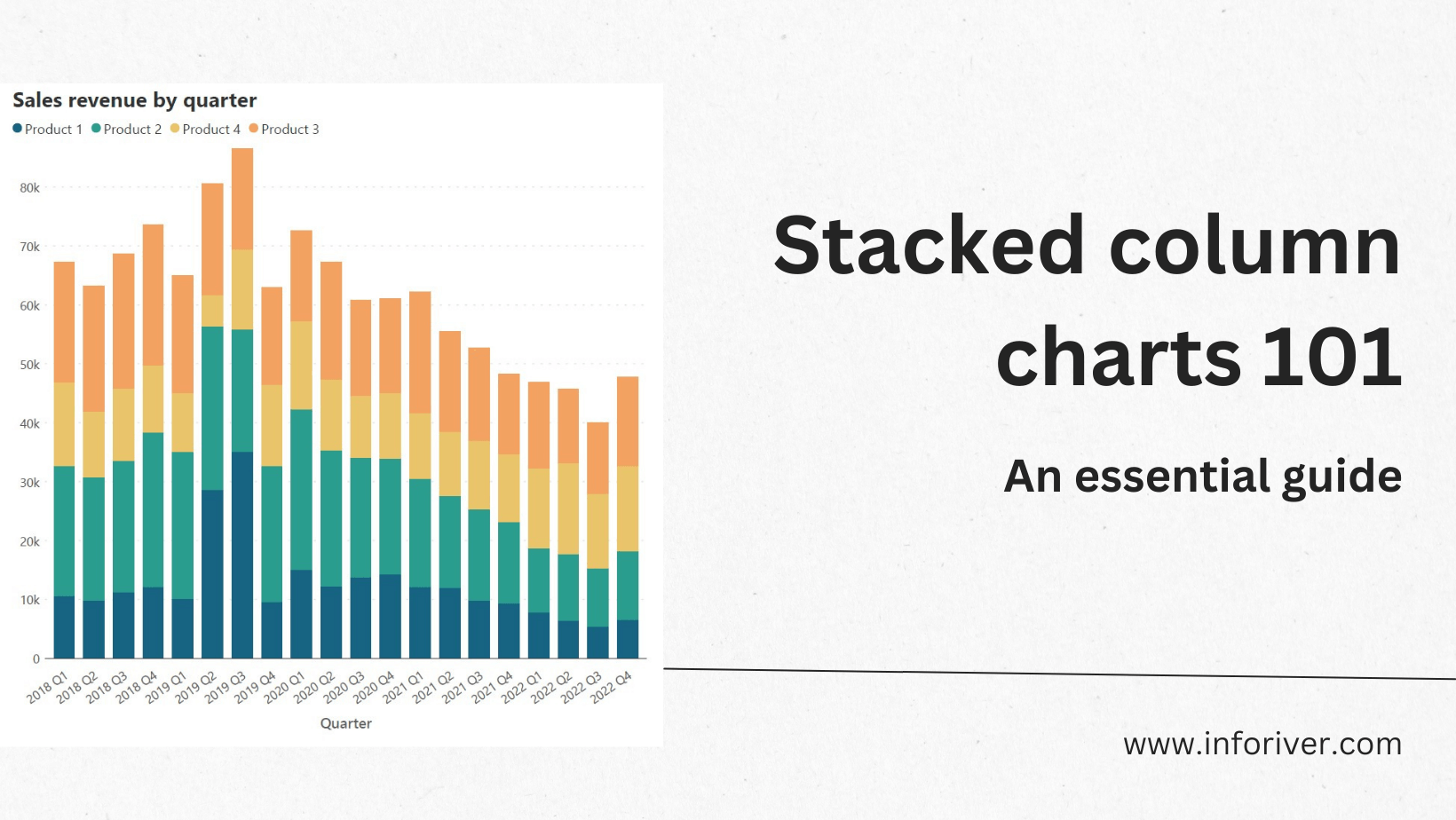
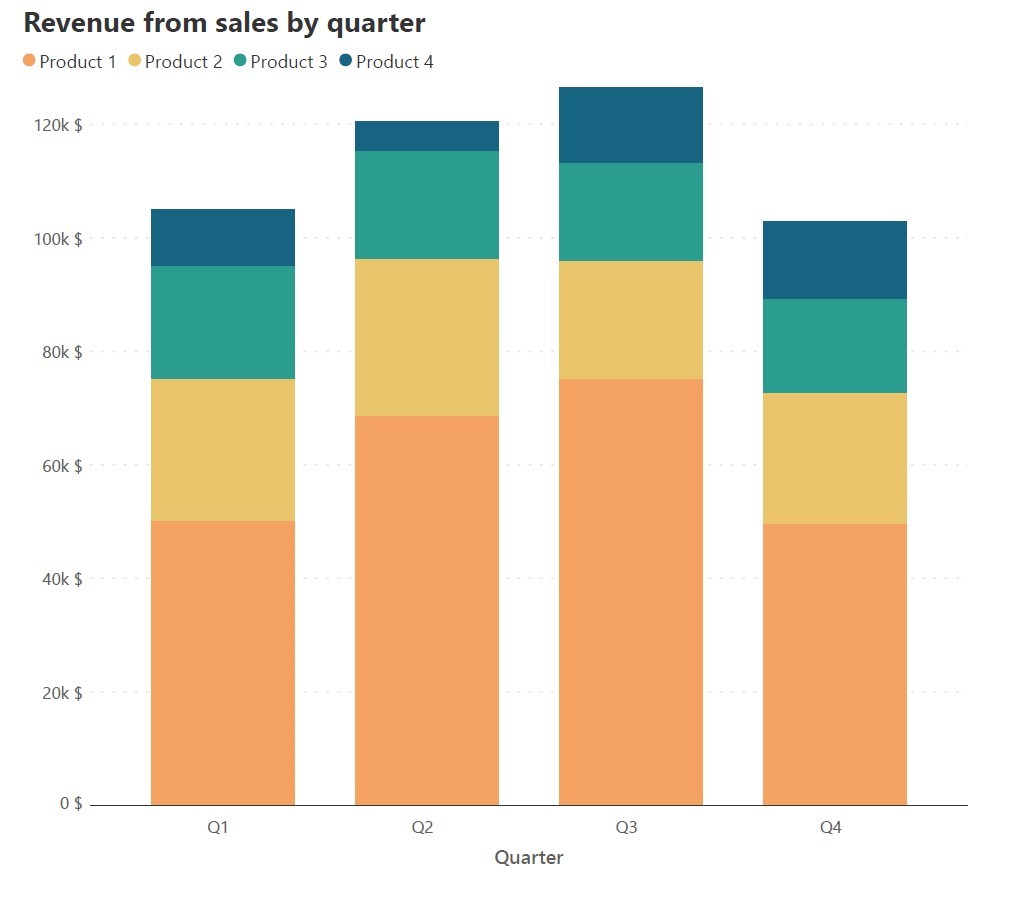
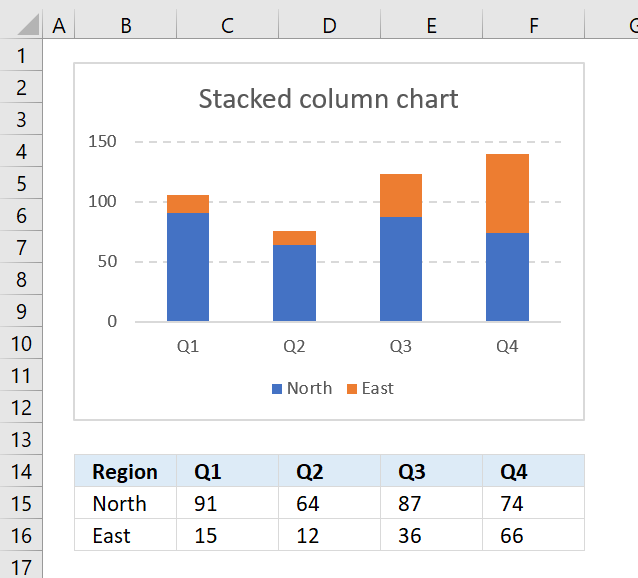
For instance, below is the sales revenue for four quarters of three units of an organization. But, as the number of data series increases, the complexity of representation also increases. The answer to this question depends on what you require from the chart.
Marketing (spending vs results) economy (supply and demand) vehicle performance (mileage vs performance) business budgets (spending vs saving) A stacked column chart in excel is a column chart where multiple series of the data representation of various categories are stacked over each other. One popular yet powerful type of data visualization is the stacked column chart.
A stacked bar chart shows two categorical variables. Understanding when to use stacked column charts is crucial for effective data visualization. When do you use a stacked column chart?
The main objective of a standard bar chart is to compare numeric values between levels of a categorical variable. The first (and primary) variable is shown along the entire length of the bar, and the second variable is represented as stacks within each categorical bar. When to use stacked column charts.
One bar is plotted for each level of the categorical variable, each bar’s length indicating numeric value. Learn when to use and avoid stacked column charts for effective data visualization. When to use stacked column charts.
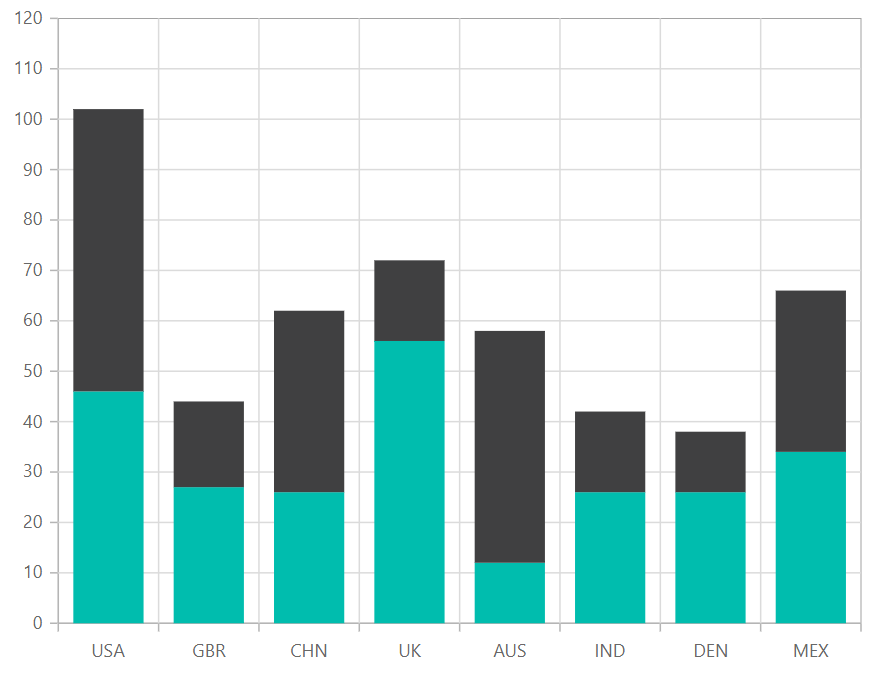
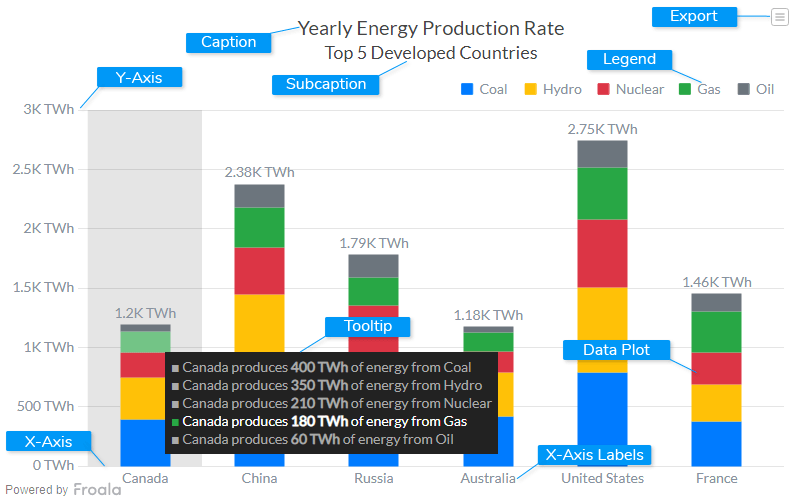
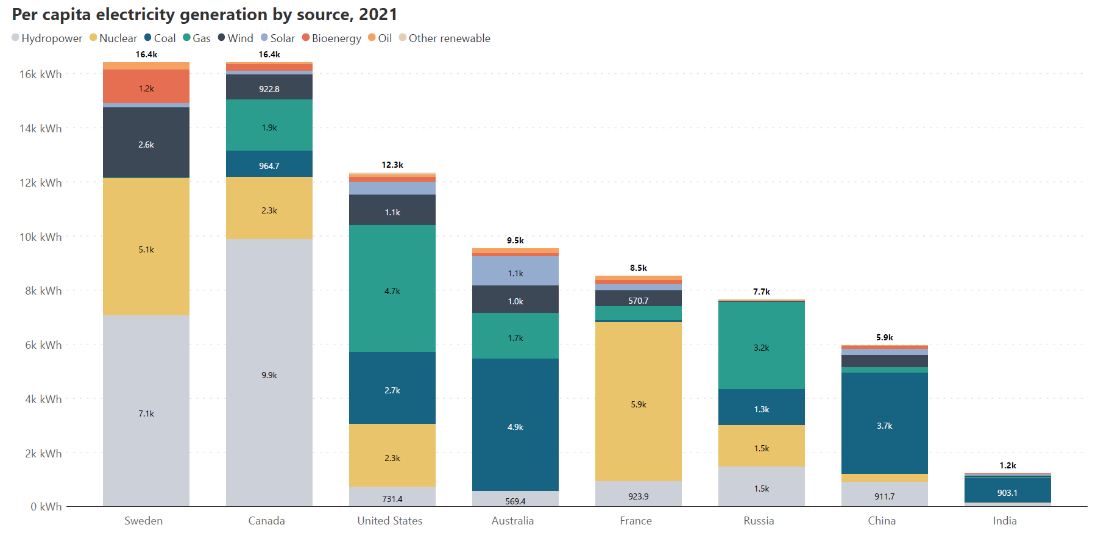
A stacked bar chart also achieves this objective, but also targets a second goal. A stacked column chart in excel compares parts of a whole over time or across categories. Consider the chart below, for example.
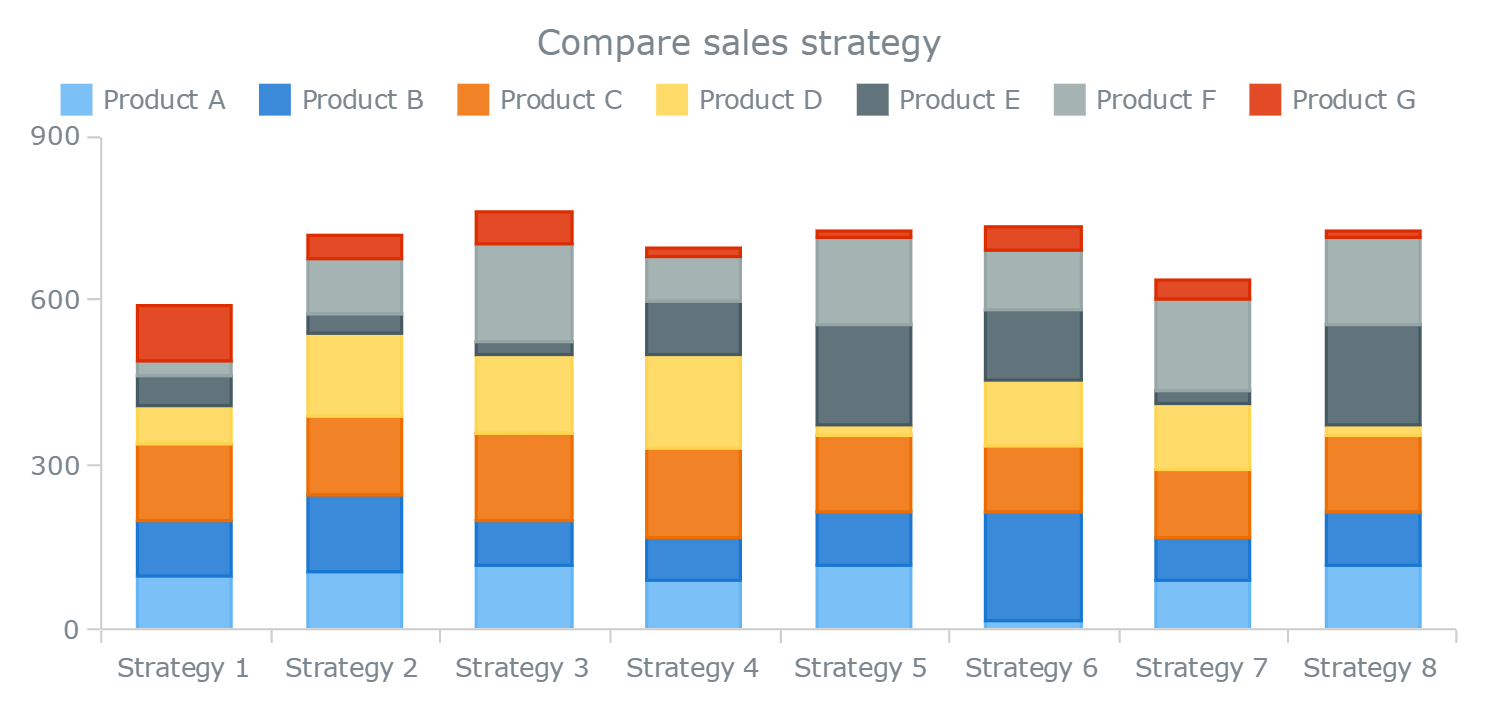
Stacked column chart is useful to compare multiple dimensions against a single measure. If you feel inspired after the read, you can create both stacked column and stacked bar charts in our charting tool datawrapper. Stacked bar charts are designed to help you simultaneously compare totals and notice sharp changes at the item level that are likely to have the most influence on movements in category totals.
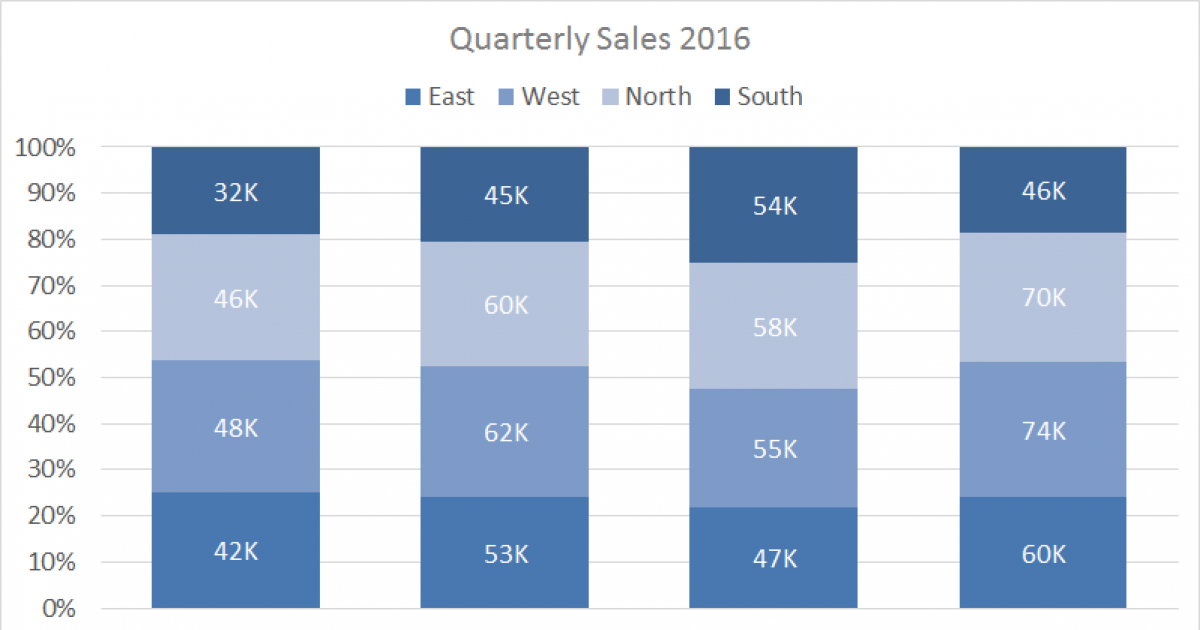
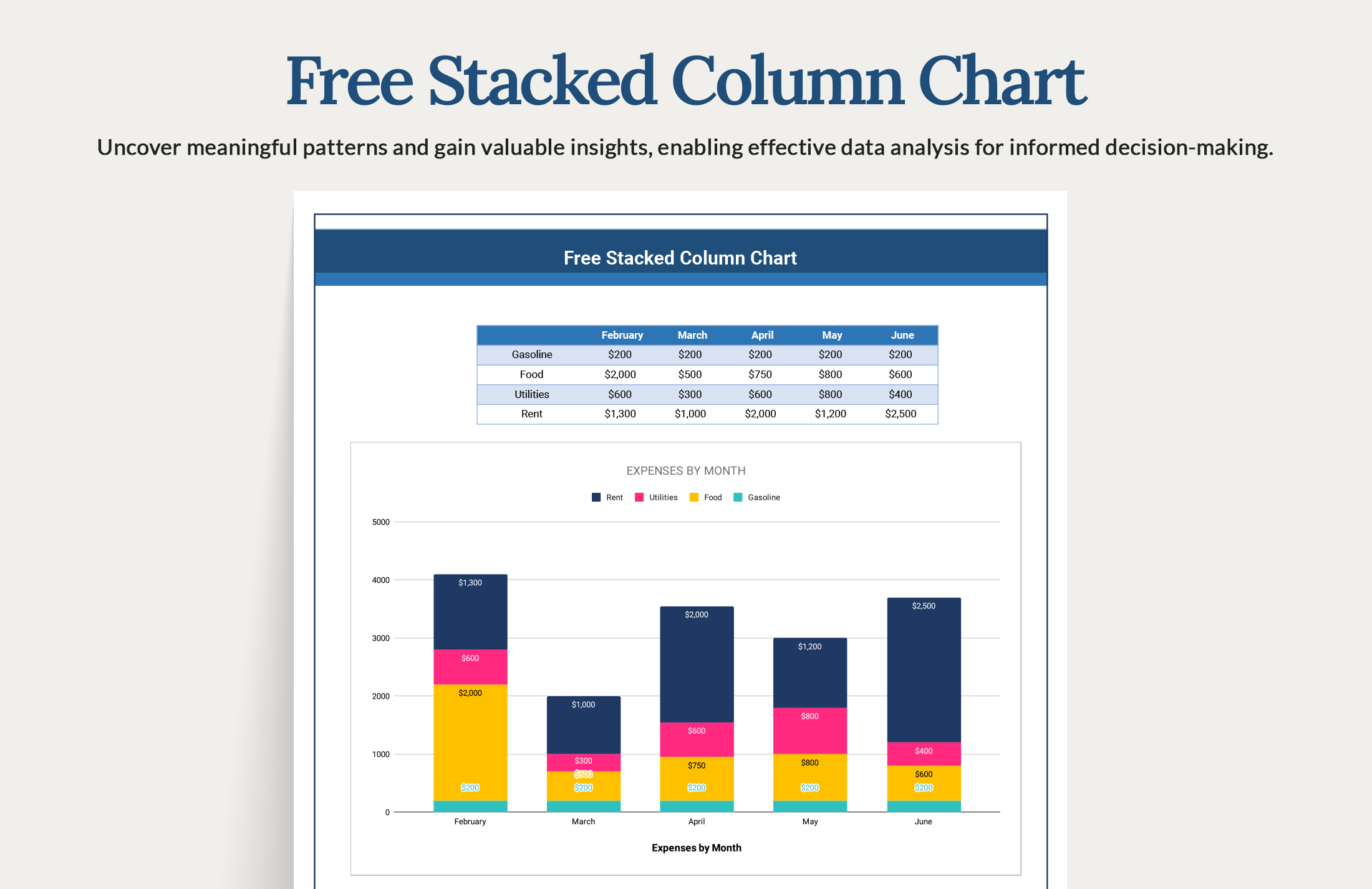
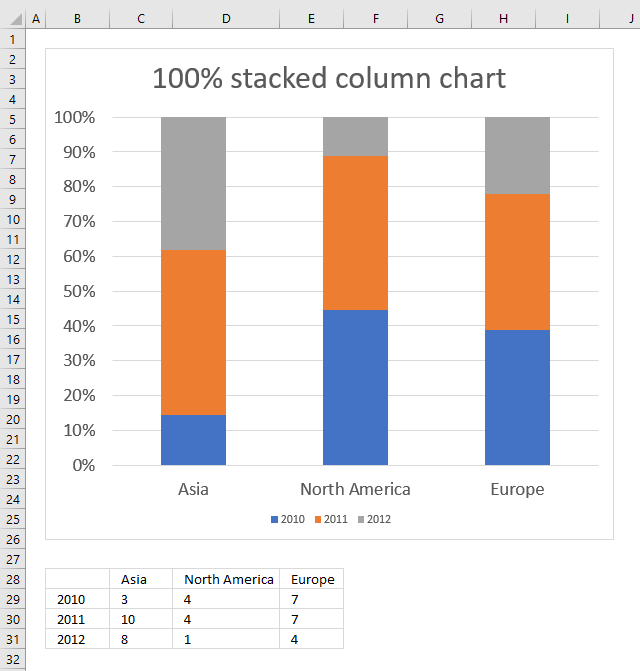
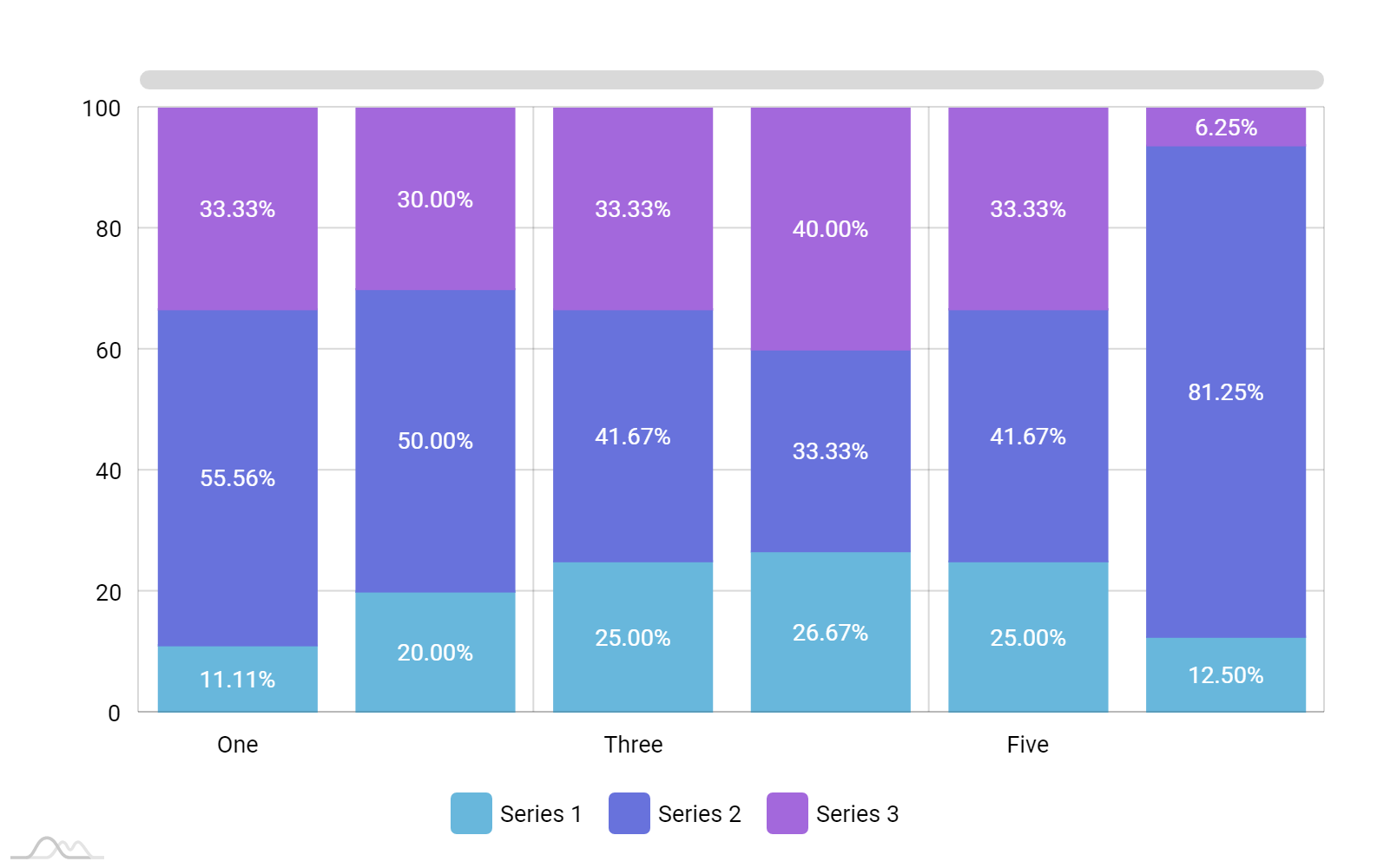
If the goal is to show relative differences within each group, use a stacked percentage column chart. Let’s look at an example. Download the workbook, modify data, and practice.
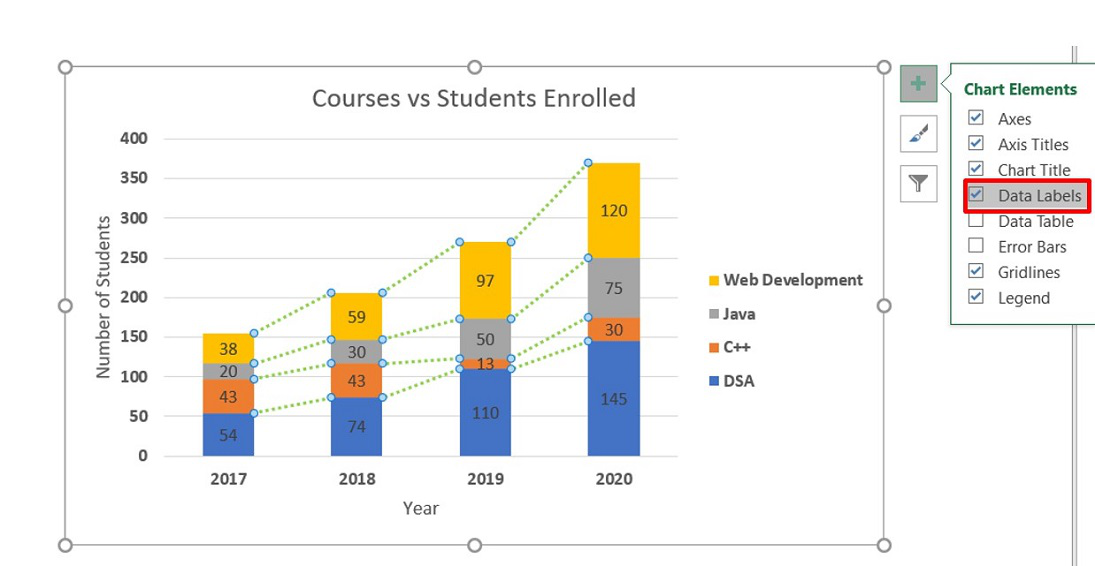
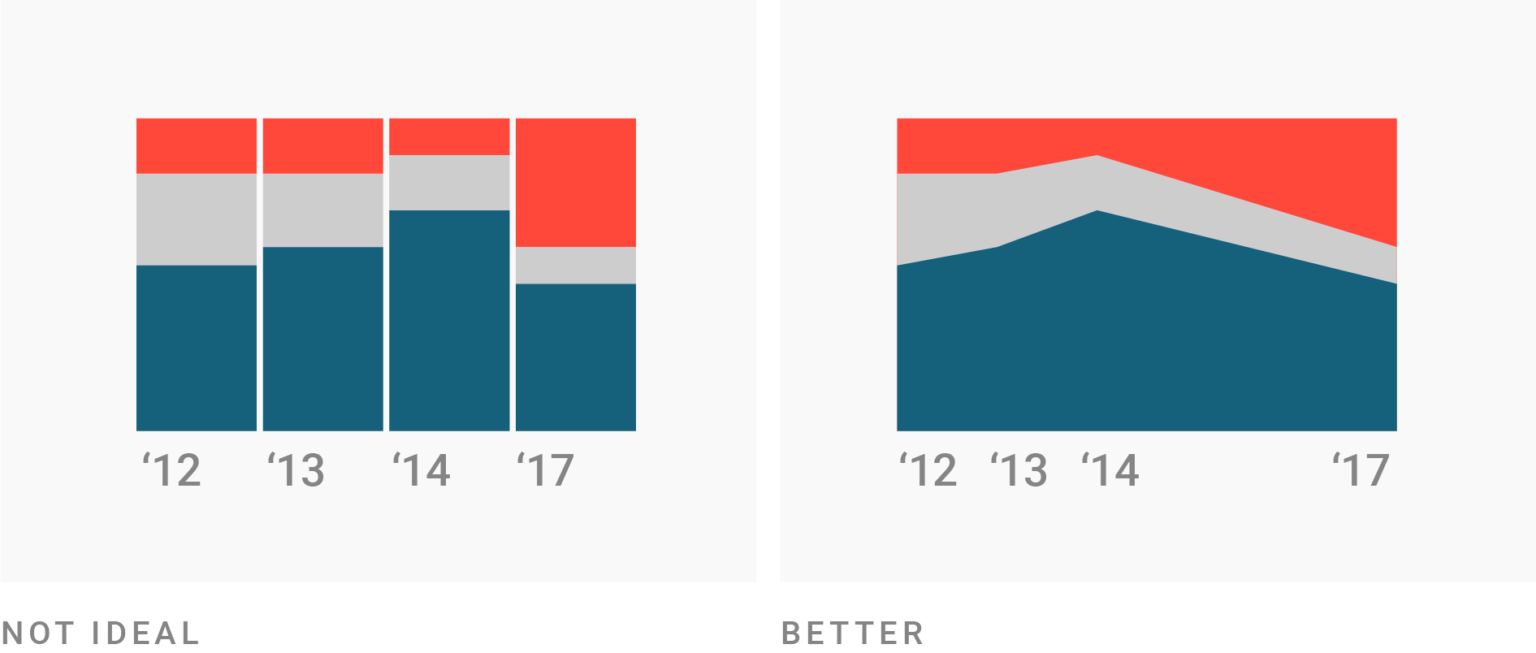
In a stacked column chart, the vertical axis represents the numerical values of the data, while the horizontal axis displays the categories or time periods. The comparison for numerous data series is easy. While a stacked column chart uses vertical bars stacked on top of each other, a stacked area chart stacks multiple area series on top of each other.